Half of Venezuela’s oil rigs may disappear if US waivers lapse
(Bloomberg) — A looming U.S. sanctions deadline is threatening to clobber Venezuela’s dwindling oil-rig fleet and hamper energy production in the nation with the world’s largest crude reserves.
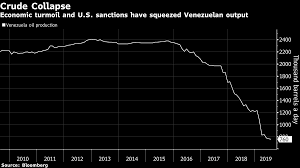
Almost half the rigs operating in Venezuela will shut down by Oct. 25 if the Trump administration doesn’t extend a 90-day waiver from its sanctions, according to data compiled from consultancy Caracas Capital Markets. That could further cripple the OPEC member’s production because the structures are needed to drill new wells crucial for even maintaining output, which is already near the lowest level since the 1940s.
A shutdown in the rigs will also put pressure on Nicolas Maduro’s administration, which counts oil revenues as its main lifeline. The U.S. is betting on increased economic pressure to oust the regime and bring fresh elections to the crisis-torn nation, a founding member of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and Latin America’s biggest crude exporter until recent years.
Venezuela had 23 oil rigs drilling in July, down from 49 just two years ago, data compiled by Baker Hughes show. Ten of those are exposed to U.S. sanctions, according to calculations by Caracas Capital Markets. The Treasury Department extended waivers in July for service providers to continue for three more months, less than the six months the companies had sought.
Most other government agencies involved in the deliberations opposed any extension, a senior administration official said last month, adding that another reprieve will be harder to come by.
“Almost half the rigs are being run by the Yanks, and if the window shuts down on this in two months, then that’s really going to hurt Venezuela unless the Russians and the Chinese come in,” said Russ Dallen, a Miami-based managing partner at Caracas Capital Markets.
Output Risk
A U.S. Treasury official said the department doesn’t generally comment on possible sanctions actions.
More than 200,000 barrels a day of output at four projects Chevron Corp. is keeping afloat could shut if the waivers aren’t renewed. That would be debilitating to Maduro because the U.S. company, as a minority partner, only gets about 40,000 barrels a day of that production.
The departure of the American oil service providers would hurt other projects in the Orinoco region, where operators need to constantly drill wells just to keep output from declining. The U.S.-based companies are also involved in state-controlled Petroleos de Venezuela SA’s joint ventures in other regions such as Lake Maracaibo.
Limiting Exposure
Halliburton Co., Schlumberger Ltd. and Weatherford International Ltd. have reduced staff and are limiting their exposure to the risk of non-payment in the country, according to people familiar with the situation. The three companies have written down a total of at least $1.4 billion since 2018 in charges related to operations in Venezuela, according to financial filings. Baker Hughes had also scaled back before additional sanctions were announced earlier this year, the people said.
Schlumberger, Baker Hughes, Weatherford, PDVSA and Venezuela’s oil ministry all declined to comment.
Halliburton has adjusted its Venezuela operations to customer activity, and continues operating all of its product service lines at its operational bases, including in the Orinoco Belt, it said in an emailed response to questions. It works directly with several of PDVSA’s joint ventures, and timely payments from customers are in accordance with U.S. regulations, it said.
Hamilton, Bermuda-based Nabors Industries Ltd. has three drilling rigs in Venezuela that can operate for a client until the sanctions expire in October, Chief Executive Officer Anthony Petrello said in a July 30 conference call, without naming the client.
The sanctions carry geopolitical risks for the U.S. If Maduro manages to hang on, American companies would lose a foothold in Venezuela, giving Russian competitors such as Rosneft Oil Co. a chance to fill the void. Chinese companies could also benefit. Even if the waivers get extended, the uncertainty hinders any long-term planning or investments in the nation by the exposed companies.
Rosneft’s press office didn’t respond to phone calls and emails seeking comment on operations in Venezuela.
–With assistance from David Wethe, Debjit Chakraborty and Dina Khrennikova.
To contact the reporters on this story: Peter Millard in Rio de Janeiro at pmillard1@bloomberg.net;Fabiola Zerpa in Caracas Office at fzerpa@bloomberg.net
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Tina Davis at tinadavis@bloomberg.net, Pratish Narayanan, Joe Ryan
For more articles like this, please visit us at bloomberg.com
©2019 Bloomberg L.P








