The true cost of ocean plastic pollution
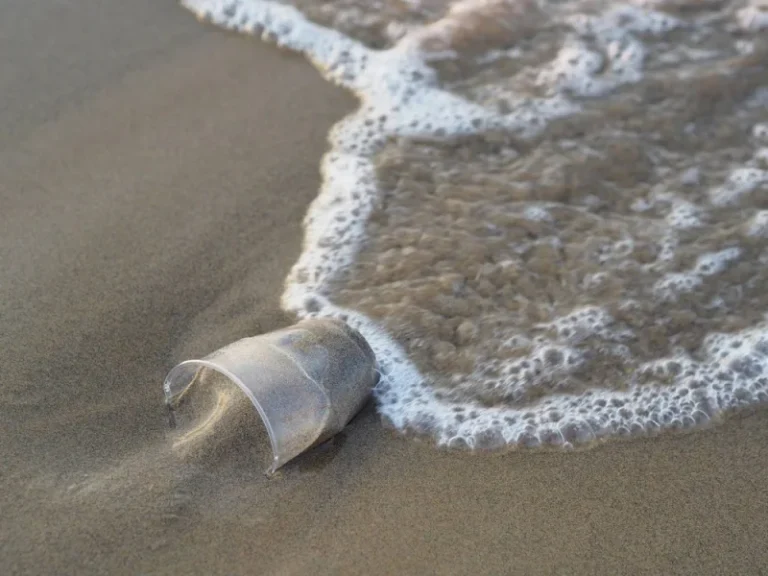

The problem of maritime plastic-waste pollution first became apparent in the 1970s. In the half-century since then, the problem has become ever more widespread, as scientific expeditions conducted by the Tara Ocean Foundation (of which I am executive director) have shown. Large pieces of debris, such as fishing nets, and their disastrous effects on marine life, are the most visible symptom. Such waste is estimated to kill more than one million seabirds and over 100,000 marine mammals annually, often through entanglement or suffocation, and promotes transport of invasive species, triggering a cascading effect on the ecosystems in which they play a central role.
Less visible, but more pervasive, are microplastics, which have been found in the deepest ocean trenches and all types of marine life. Microplastics can, among other things, modify bacterial and viral communities and disperse chemical toxins in food chains (often after being ingested by marine organisms). Some of these toxins, such as phthalates, are associated with the chemistry of plastics, while others, such as pesticides and heavy metals, are absorbed by the plastic before it reaches the ocean and enters the food chain.
How these toxic substances interact with plastics has been the subject of much study. Plastic is comprised of monomers that have been chemically bonded to form long chains of polymers – ethylene, styrene, and propylene become polyethylene, polystyrene, and polypropylene. But the process of polymerisation is often imperfect, and some of the unpolymerised monomers that remain in plastic, like different types of styrene and bisphenol, pose major environmental and health risks.
Moreover, other chemical additives, including plasticisers, fillers, colorants, flame retardants, and antioxidants, are incorporated into polymer formulations to modify their properties. And non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) – impurities, raw materials used in manufacturing, byproducts, and degradation products – bind to finished plastics. In most cases, because free monomers, additives, and NIAS are simply trapped within the tangle of polymer chains, rather than being chemically bound to them, they are more likely to leach out during the production, use, and disposal of plastic, migrating into liquids, gases, and solids. Some 16,000 such molecules have been identified, but their effects are still not fully known, nor is their toxicity, which can change depending on how they are combined. What we do know is that one-quarter of these 16,000 molecules are pose a hazard to human health or the environment by disrupting biochemical processes in living organisms.
Halting the flow of microplastics and toxic pollutants into the world’s bodies of water is a Sisyphean task. Nevertheless, scientists are trying to stem the problem. For example, the Tara Europa expedition, in coordination with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and more than 70 scientific institutions across the continent, has spent the past two years investigating how these hazardous substances make their way into the seas and oceans bordering Europe. The mission plans to share its findings soon.
But the generation of toxic waste and debris is not the only way that plastic can harm ocean health. The plastics industry has been a major driver of climate change, accounting for an estimated 3.4% of global greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions. Plastic production is on track to contribute 15% of GHG emissions by 2050, exacerbating global warming and thereby increasing the threats to marine life, which is sensitive to rising water temperatures.
Because plastic degrades the entire biosphere, not just the ocean, it is not a waste problem that can be solved by a few sustainability-minded citizens’ recycling efforts. This is a systemic crisis that requires an economy-wide solution. A better approach is to understand plastic as one of the “new entities” that must not leak into the environment, a view initially formulated by the Stockholm Resilience Centre in its work on planetary boundaries and later endorsed by the United Nations. While acknowledging the impossibility of defining a precise threshold for harm, such an approach highlights the need for a drastic reduction in plastic use.
Research suggests that it would be economically feasible to halve global plastic production at a cost which would almost surely be less than the cost of inaction. But, according to a recent study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, even this reduction would not be enough to limit global warming to 1.5° Celsius above preindustrial levels, the target set by the Paris climate agreement. Instead, they found that meeting this goal would require a 75% reduction in plastic production compared to 2015.