“Climate crisis gives Greece and Turkey opportunity for ‘historic compromises”
By: Roudi Baroudi – Washington D.C. 23 June 2021
Greece and Turkey have one of the world’s most complicated relationships. We all know the history, although many of the details are contested by dueling narratives. However we got here, some indisputable facts are clear. Two former long-time enemies were thrown together as allies by the Cold War, when both of them joined NATO, but have generally remained at odds over a long list of issues.
The essential lesson from this simple synopsis is that Greece and Turkey joined the Atlantic alliance for the same core reason: each viewed their feud as a lesser threat than the one posed by the Soviet Union, which was potentially existential. At the end of the day, and despite both age-old resentments and ongoing tensions, successive governments – including military juntas – of both countries abided by the same rational analysis for decades.
Both are still NATO members, but the Soviet threat is no more, replaced only partially by a far weaker Russia. To some extent, this has led to a resumption of Greco-Turkish friction, especially over their maritime boundaries in the Mediterranean. And this time, there is much more than either pride or territory at stake. Since huge amounts of offshore natural gas have been discovered in several parts of the Eastern Med, the border dispute may well involve resources that could confer historic advantages on whoever controls them.
Once again, these sound like rational calculations. But are they really? I will allow that large reserves of natural gas have the potential to help any country secure a better future for its people. The savings and revenues would allow unprecedented investments in education, healthcare, transport, and other infrastructure, creating more and better jobs and lifting countless people out of poverty. Even the transit fees from hosting an international pipeline can provide significant income, and the more territory a pipeline crosses, the higher the fees.
But ladies and gentlemen, I would submit that, as was the case during the Cold War, both Greece and Turkey would do well to take fuller account of larger – in fact, much, much larger – considerations. And all of them have to do with climate change. This challenge constitutes a mortal threat, not only to Greeks and Turks, but also to human civilization itself. And unlike the Soviet Union, this is not a politico-military power that can be deterred, mollified, or reasoned with. Nor can we wait it out and hope that, like the USSR, climate change will be torn apart by its own flaws.
No, we will only save our planet by working together to undo the damage we have done by pumping endless streams of carbon into the atmosphere. We can only do that by drastically reducing emissions, and that can only be accomplished by transitioning to renewables and cleaner, greener fuels. And like it or not, as major Mediterranean powers, Greece and Turkey have enormous roles to play in this process – and therefore enormous responsibilities. As in NATO, both will be expected to pull their respective weights.
As a result of all this, Greece and Turkey once again face a common and potentially existential threat. Energy is a crucial consideration in combating this threat, but the acreage that matters most in the long term is no longer on the seafloor. Instead, it is on the surface, where offshore wind and solar parks figure to provide much of the electricity required to reduce, and eventually end, reliance on hydrocarbons.
The sea will abet decarbonization efforts in other ways, too, by hosting multiple clean energy activities and technologies that help reach the Paris Agreement goal of “Net Zero” carbon emissions by 2050. The options include wave, rain, and tidal power; undersea geothermal; and, yes, natural gas, which is cleaner than other fossil fuels and can be expected to persist for a considerable time as a transition fuel. In addition, no coastal country can ignore the potential of “Blue Carbon”: if we restore and maintain the health of coastal and marine ecosystems, they will naturally remove more and more carbon from the atmosphere.
But here is the thing. Implementation of offshore energy projects will be slowed, or even indefinitely postponed, if Greece and Turkey continue on their current course. Even if they agree to reduce tensions but fail to settle or suspend their differences, the uncertainty will steer many investors to less troubled waters. By contrast, if they find a way to truly put the past behind them, both countries’ decarbonization efforts will be vastly more attractive. As a result of an earlier and stronger start, they will also be more effective – exponentially so if they take the next step and actively cooperate, especially on maritime issues.
The sea is a wondrous place filled with many things we need, many we simply love, and others that we have yet to discover. It is also, however, a veritable and pitiless force of nature: what it cannot violently destroy in an instant, it will inevitably erode, undermine, and dissolve over time. We now have technologies to make far more – and far more responsible – use of the sea than ever before, but its very nature makes most undertakings more difficult and potentially dangerous than on land. And as any sailor knows, the best tools we have to predict, avoid, and/or overcome whatever the sea throws at us are information and cooperation.
As neighbors in this shared space and de facto partners in the campaign to reduce emissions, Greece and Turkey could maximize the return on their efforts, both individual and combined, by working together. Given the importance of information and the rate at which our ability to gather it is growing due to technology, the natural place to start would be comprehensive data-sharing. For almost anything built, installed, and/or operated at sea, advance knowledge of weather conditions, tides, currents, water temperatures, salinity levels, etc., can be crucial for planning, performance, and the protection of both human beings and the environment. Wind and solar parks are no exceptions, and neither are numerous other activities in the Blue Economy, including maritime transport, aquaculture, conventional fisheries, tourism, seabed mining, and bio-prospecting.
In addition to activating commercial, efficiency, safety, and environmental gains, cooperation in these fields would also help build trust, but operational coordination and regulatory harmonization would go even further. In the best-case scenario, Greece and Turkey would both reap significant benefits by expanding into joint compliance and enforcement work, streamlining cross-border trade and investment, easing the migrant crisis, and addressing numerous other issues of mutual concern.
To get there, both Athens and Ankara need to take strategic decisions which, one way or another, insulate their present and future relationship against all extraneous considerations. And more than one clock is ticking. In addition to the 2050 target date for Net Zero carbon, an even more pressing deadline attaches to the region’s natural gas prospects. In a report for consideration during the UN Climate Conference, COP 26, at Glasgow in November, scientists have recommended that if we are to meet the 2050 goal, development of new oil and gas fields should not be permitted beyond the end of this year. It is too early know whether that deadline will be adopted, but the writing is on the wall: apart from those that have already started – Egypt, Israel, and to some extent Cyprus – if East Med countries want to profit from their offshore hydrocarbons, they need to make meaningful progress very soon.
For several countries in the region, the primary obstacle is that most of its maritime boundaries remain in dispute or otherwise unresolved, so their claimed Exclusive Economic Zones overlap. With Greece and Turkey, the overlap is considerable.
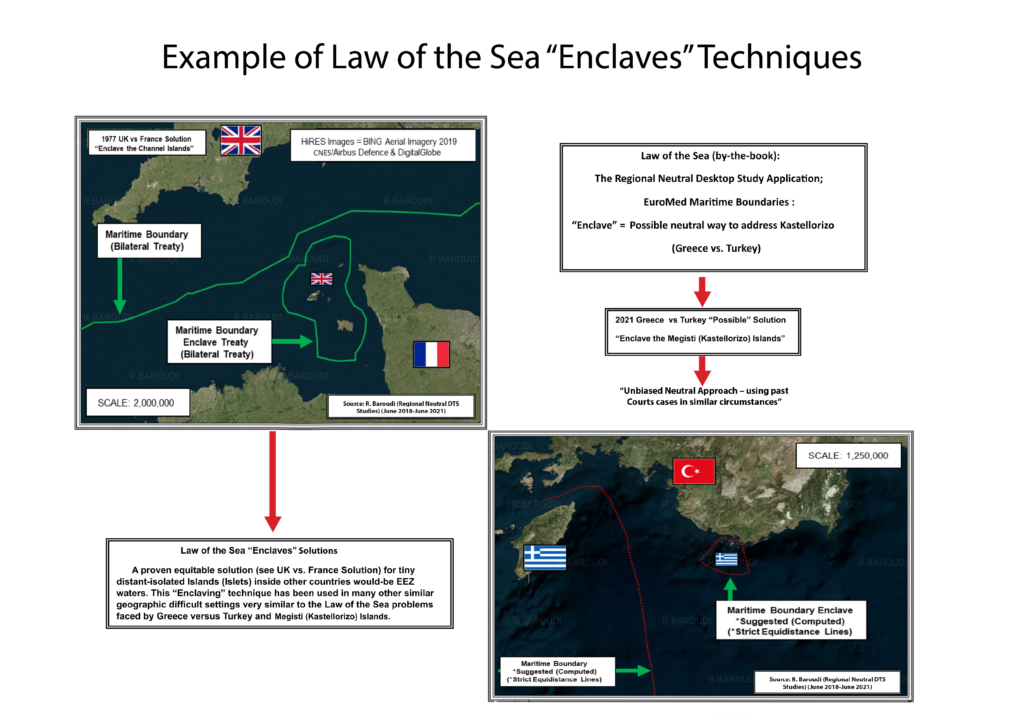
But even this obstacle can be surmounted if there are sufficient amounts of both goodwill and self-interest. Both Greece and Turkey need to make the most of the Blue Economy, but neither will realize its full potential unless and until it helps the other do the same. The UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, or UNCLOS, lays down a comprehensive assortment of legal and scientific standards for the fair and equitable drawing of borders at sea, and these apply to both member and non-member states. Whatever mechanism the parties use to settle their boundary dispute, whether it’s direct negotiations, an international court, or some form of arbitrations, the same rules apply.
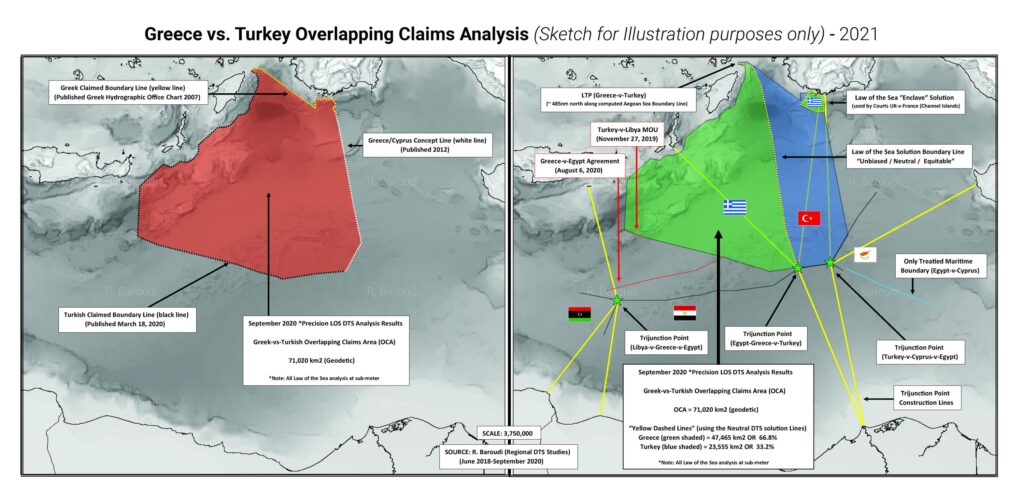
Ideally, Greece and Turkey would mount an all-out effort to recognize the relevant limits of their respective EEZs. It may be too late to succeed before a moratorium on new gas development is declared, but even if that is the case, they will still need in certain areas EEZ clarity to maximize both their offshore renewables and the non-energy components of their Blue Economy industries. In addition, they also have the option of circumventing the EEZ issue, allowing them to develop subsea gasfields and share the proceeds, while temporarily putting their territorial dispute in abeyance. Even if that fails too, the mere attempt might improve relations, establishing a basis for the cooperation described above.
Previous attempts at reconciliation have always fallen short or been derailed, but there is reason to hope that the time is right for a new effort, and that some of the key players are in the right frame of mind. Last week’s NATO summit, for instance, saw US President Joe Biden hit very different notes than his predecessor, Donald Trump, by stressing the alliance’s potential to influence a wide variety of geopolitical issues. His meetings on the sidelines of the summit included one with his Turkish counterpart, Recep Tayyip Erdogan, who later described their conversation as having opened a “new era” of constructive ties. If that turns out to be true and Ankara really wants to repair its relations with Washington, it could have positive ramifications, not only for Greco-Turkish reconciliation, but also for a peaceful resolution of the Cyprus issue.
In the final analysis, both Greece and Turkey have everything to gain, and nothing or relatively little to lose, by cooperating at every opportunity, but especially on various forms of energy. As with their respective decisions to join NATO, this will require clear-headed analysis and pragmatic policymaking, but also the sangfroid to reach, promote, defend, and implement some historic compromises.
Roudi Baroudi has more than 40 years of experience in the energy business and has helped design policy for major international oil companies, sovereign governments, and multilateral institutions. He currently serves as CEO of Energy and Environment Holding an independent consultancy based in Doha, Qatar.

Roudi Baroudi has more than 40 years of experience in the energy business and has helped design policy for major international oil companies, sovereign governments, and multilateral institutions. The author or co-author of several books, his latest was “Maritime Disputes in the Mediterranean: The Way Forward” (2020), and his next – a study of the region’s Blue Economy prospects in the post-carbon era – is expected to come out in the first half of 2022. He currently serves as CEO of Energy and Environment Holding, an independent consultancy based in Doha, Qatar.