The biggest news in the energy industry last week was that a state-owned Chinese company had completed a massive offshore oil and gas platform for Saudi Aramco. Breathless media reports shared impressive details about the facility’s record-setting size, weight, and output capacity, with some describing it as a massive bet on continuing strong demand for fossil fuels despite the meteoric rise of renewables.
The real significance of this news, though, is not to be found at the Qingdao shipyard where it was made, at the headquarters of the China Offshore Oil Engineering Company that built it, or at the Marjan field off Saudi Arabia’s east coast where it will be installed and operated.
In fact, in order to truly appreciate the implications involved, one needs to travel back in time a little more than 50 years. For on 8 June 1974, the United States and Saudi Arabia reached a historic agreement that has bound the two countries ever since.
Signed by then-US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger and then-Minister of Interior Prince Fahd bin Abdulaziz, the pact established two joint commissions tasked, respectively, with increasing bilateral economic cooperation and with determining the kingdom’s military needs. It also created several joint working groups responsible for specific elements to support growth and development, including efforts to: a) expand and diversify Saudi Arabia’s industrial base, beginning with the manufacture of fertilizers and other aspects of the petrochemical sector; b) increase the number of qualified scientists and technicians available to make the most of technology transfers; c) explore partnerships in areas like solar energy and desalination; and d) find ways to cooperate in agriculture, especially in the desert.
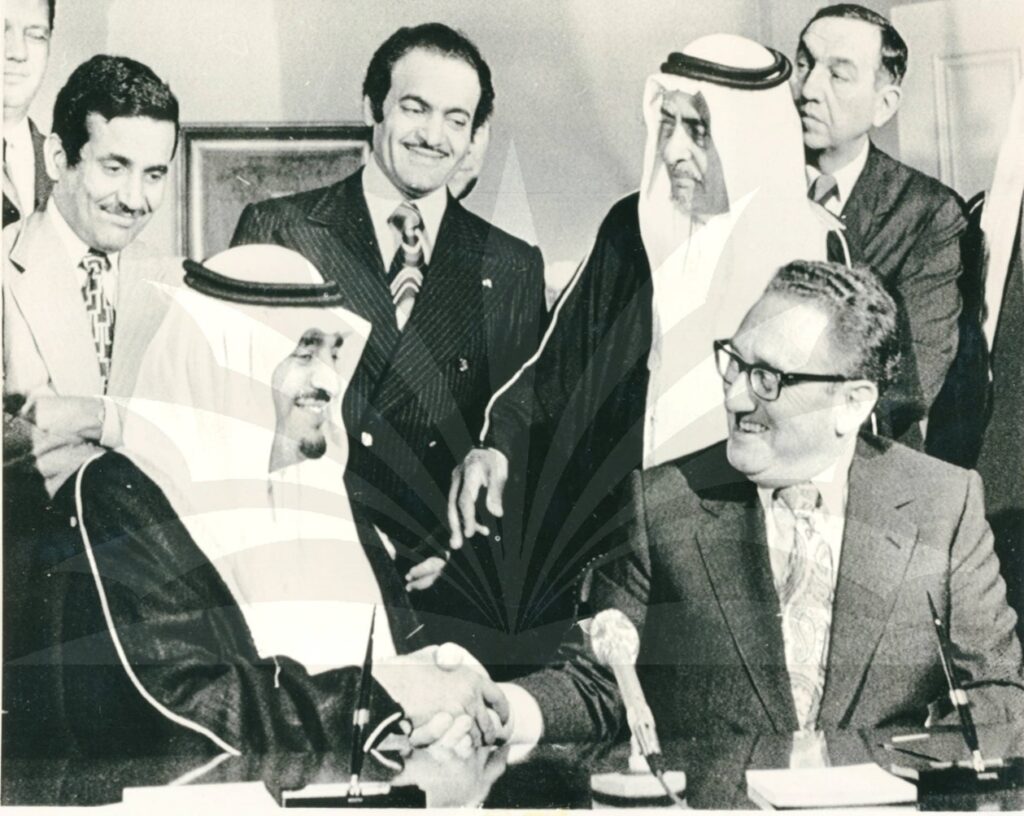

Henry Kissinger with Prince Fahd of Saudi Arabia, 1974
Contrary to widespread misperceptions, the agreement did not say anything about Saudi crude being priced and/or transacted exclusively in US dollars. In a side-deal that remained secret until 2016, however, the United States pledged full military support in virtually all circumstances and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia committed to investing a massive share of its oil revenues in US Treasury bills. While there was no public quid pro quo, therefore, this was to some extent a distinction without a difference: the world’s biggest oil exporter ended up spending hundreds of billions of dollars on American debt and American-made weapons, making it only sensible that the vast majority of its crude sales would be in greenbacks. By extension, the sheer weight of Saudi oil in world markets – and especially within the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries – virtually guaranteed that the dollar would become the de facto default currency of those markets, Petrodollars.
These arrangements suited both sides at the time, which featured a very particular set of circumstances. The previous year, as Egypt and Syria attempted to regain territories occupied by Israeli forces since the 1967 war, US President Richard Nixon authorized an unprecedented airlift of weaponry – everything from tanks, artillery, and ammunition to helicopters, radars, and air-to-air missiles – to Israel. Arab oil producers responded by playing their strongest card, announcing an oil embargo against states that supported the Israeli war effort. That led directly to supply shortages, soaring prices, and long lines at filling stations across the United States and many other countries, too, and indirectly to several years of higher inflation. Although the embargo had been lifted in March 1974, Washington was keen to prevent similar shocks in the future.
The American economy was particularly vulnerable to longer-term repercussions because of several factors, including a general slowdown caused by its long, expensive, and ultimately unsuccessful war in Vietnam. The real problem, though, stemmed from another issue: in 1971, as the dollar continued to lose ground against major European currencies, Nixon had taken the United States off the gold standard, gutting the Bretton Woods arrangements put in place after World War II and throwing foreign exchange markets into disarray. With the Cold War as backdrop, America appeared to be losing ground in its strategic competition with the Soviet Union.
The so-called “side-deal”, then, was actually far more important than the public agreement because it would restore the dollar’s primacy in international markets, making it once again the world’s favorite reserve currency, while simultaneously reducing the likelihood of future Arab oil embargos. The new system worked very well for a very long time: the US economy regained its stability, and Saudi Arabia embarked on a long program of socioeconomic development that continues to this day. Even as the Americans have sought further protection by reducing their reliance on Saudi and other OPEC crude, their bilateral partnership and the dollar’s general prevalence in the oil business have likewise persisted despite all manner of diplomatic spats, crises, and other obstacles.
Back in the present-day, the Soviet Union is no more, and although the United States has an even more formidable strategic rival in China, this competition carries neither the day-to-day intensity nor the seeming inevitability of nuclear Armageddon that the Cold War engendered. In addition, the United States is now producing more crude oil than any country ever has, further insulating its economy against exogenous shocks, while China’s rapid expansion has made it the world’s most prolific energy importer. In fact, Washington is years into a “pivot to Asia” that will see it focus less attention on the Middle East.
Meanwhile, Saudi Arabia is now led by Crown Prince, Mohammed bin Salman (MBS), a young and highly ambitious ruler who has shown himself more than willing to act independently of American desires or even demands. Accordingly, it should not surprise anyone that the behemoth facility now being transported to Marjan is just the most visible tip of the Sino-Saudi iceberg. Theirs is a burgeoning relationship driven by complementary needs, with both parties investing in one another’s economies and cooperating on large-scale energy and industrial projects.
Given all of the foregoing, it is much too early to declare the end of an era. Even if rumors that the Saudis will soon start selling oil futures contracts in yuan or other currencies turn out to be true and the results include an erosion of the dollar’s value, the US-Saudi economic relationship remains very much in place, as do defense ties ranging from procurement and maintenance to joint exercises and training. This is not to mention the approximately 60,000 Saudi students who study at American universities every year, or the countless other business and/or personal ties nurtured over decades.
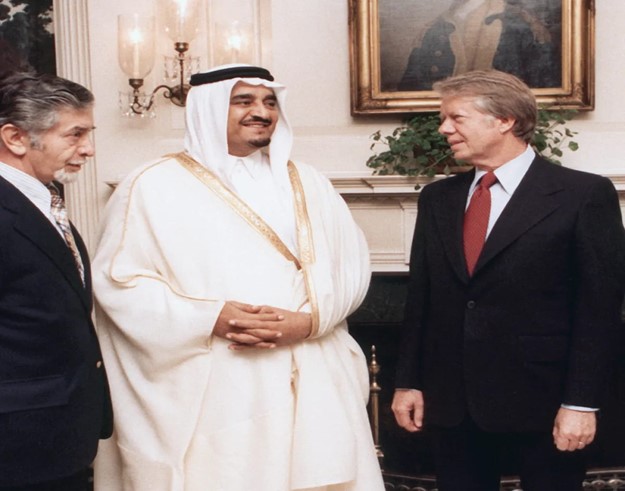

Then, US President, Jimmy Carter receiving the Crown Prince Fahd of Saudi Arabia at the White House in Washington, 1977. Seeing the continuation of the Petrodollar Agreement.
All the same, a new era has definitely begun: just as the Americans have opened up other avenues to secure their energy needs, the Saudis are now moving decisively to diversify their foreign partnerships and have been doing so for many years. Inevitably, the global oil and gas economy’s center of gravity will shift eastward, but how could it be otherwise when China and several other Asian economies have become such powerhouses? The diversification path will almost certainly include occasional stretches where Riyadh will have to make difficult decisions, but this, too, reflects the confidence that MBS has in his country’s ability to determine its own destiny.
Roudi Baroudi has worked in the energy sector for more than four decades, with extensive experience in both the public and private sectors. Having advised dozens of companies, governments, and multilateral institutions on program and policy development. He has been a loyal advocate for energy stability and peace. He is also the author or co-author of numerous books and articles, and currently serves as CEO of Energy and Environment Holding, an independent consultancy based in Doha, Qatar.