Wars aren’t won with peacetime economies

By Joseph E Stiglitz/New York
Politically, the G7 and likeminded countries around the world have adopted a war footing to stop Russian aggression. Russian President Vladimir Putin violated the most fundamental principle of international law by launching an unprovoked attack on another member of the United Nations – an institution created explicitly to prevent such aggression. The dangers of appeasement should be obvious. Even a little empathy should make us shudder in horror at the prospect of having to live under Putin’s rule.
It is a peculiar war. While Putin has described his project as a confrontation with the entire West, Ukrainians alone are doing all the fighting and bearing the full brunt of Russian attacks on civilians and civilian infrastructure. Meanwhile, Europe and America have provided economic and military assistance, and the rest of the world has been dealing with the war’s fallout, including higher energy and food prices.
But it is a mistake to think that the war can be won with a peacetime economy. No country has ever prevailed in a serious war by leaving markets alone. Markets simply move too slowly for the kind of major structural changes that are required. That’s why the United States has the Defence Production Act, which was enacted in 1950 and invoked recently in the “war” against Covid-19, and again to address a critical shortage of baby formula.
Wars inevitably cause shortages and generate windfall gains for some at the expense of others. Historically, war profiteers have typically been executed. But today, they include many energy producers and traders who, rather than being marched to the gallows, should be subjected to a windfall profits tax. The European Union has proposed such a measure, but it would come too late, and it is too weak and too narrow for the challenge at hand. Similarly, while several members of Congress have put forward bills to tax Big Oil’s superprofits, the Biden administration has so far failed to move on the issue.
That is understandable, given that US President Joe Biden has been busy enlisting support for signal achievements like the Inflation Reduction Act and the CHIPS Act. Moreover, in seeking the private sector’s cooperation in limiting price increases, he has been at pains not to appear “anti-business.” But taxing windfall profits and using the proceeds to finance the necessary war spending and support for those hurt by high prices is not anti-business; it is responsible wartime governance, which is necessary to maintain popular support for the war effort. Such temporary taxes hurt neither investment nor employment, and there is nothing unjust about taxing exceptional gains that companies did nothing to deserve. (Besides, more generally, taxes on corporate profits are not distortionary, because costs, including capital, are deductible.)
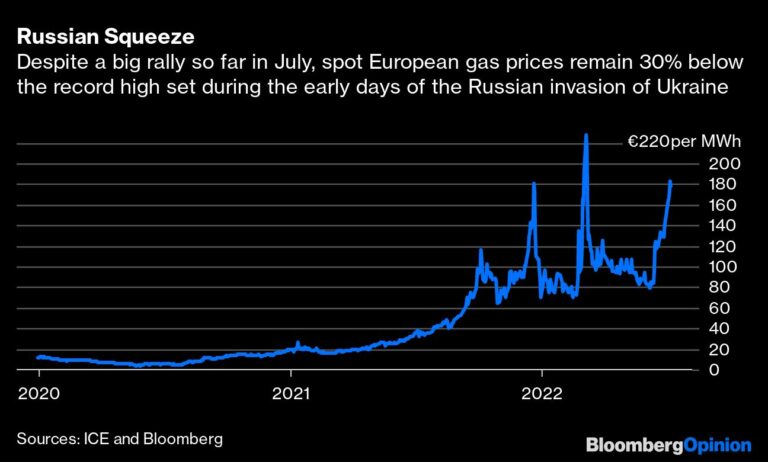
Even more comprehensive measures are needed in Europe, where today’s electricity market was not designed to deal with wartime conditions. Instead, it follows the principle of marginal-cost pricing. That means the electricity price reflects the highest-cost source of production needed to meet current demand. As gas prices have soared, marginal costs have risen far above average costs. The cost of renewable energy has, for instance, changed little.
As such, many sellers of low-cost electricity are making a killing, as are the traders who bought energy at the lower pre-war prices. While these market players reap billions of euros in profits, consumers’ electricity bills are soaring. Electricity prices in energy-rich Norway, with its enormous gas and oil reserves and hydro capacity, have increased nearly tenfold.
Meanwhile, households and small businesses are being pushed to the brink, and even some big companies have already gone bankrupt. Last month, Uniper, a large company supplying one-third of Germany’s gas, was “nationalised,” effectively socialising its massive losses. The European principle of “no state aid” has been thrown aside, mainly because European leaders moved too slowly in changing a market structure that was not designed for war.
Economists love marginal-cost pricing because it provides appropriate incentives, and because its distributive consequences tend to be small and easily manageable in normal times. But now, the system’s incentive effects are small and its distributive effects are enormous. In the short run, consumers and small businesses will have to turn down their thermostat in the winter and turn it up in the summer, but comprehensive energy-saving investments take time to plan and implement.
Fortunately, there is a simpler system (already under discussion in some countries, and already being partly implemented in others) that would retain most of marginal-cost pricing’s incentive effects without the distributive effects. Under a non-linear pricing framework, households and firms could be allowed to purchase 90% of their previous year’s supply at the previous year’s price, and 91-110% of supply at, say, 150% of the previous year’s price, before the marginal-cost price kicks in.
While non-linear pricing can’t be used in many markets – owing to the possibility of “arbitrage” (buying a good at a low price and immediately reselling it at a much higher price) – electricity is not one of them. That is why some economists (like me) have long advocated its use in cases where large market failures are having important distributive effects. It is a powerful tool that governments can and should use, especially when confronting wartime conditions.
Something also must be done about soaring food prices. After a half-century of paying US farmers not to farm (an old method of agricultural price support), we now should pay them to produce more.
Such changes have become imperative. As the Vietnamese understood, wars are won as much on the political front as on the battlefield. The purpose of the 1968 Tet Offensive was not to gain territory but to change the political calculus of the war, and it worked. Defeating Russia obviously will require more help for Ukraine. But it also will require a better economic response on the part of the West more broadly. That starts with sharing more of the burden through windfall profit taxes, controlling key prices – such as those for electricity and food – and encouraging government interventions where necessary to alleviate critical shortages.
Neoliberalism, based on simplistic ideas about how markets should operate that fail to comprehend how they actually operate, didn’t work even in peacetime. It must not be allowed to stop us from winning this war. – Project Syndicate
* Joseph E Stiglitz, a Nobel laureate in economics, is University Professor at Columbia University and a member of the Independent Commission for the Reform of International Corporate Taxation.